StudentManagerPro Developer Guide
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
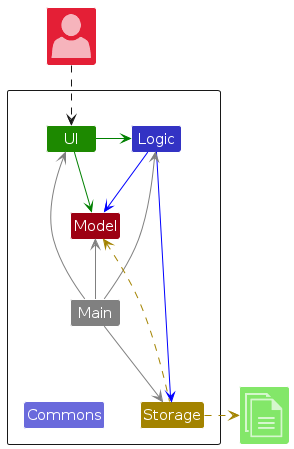
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the app.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the app.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the app in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
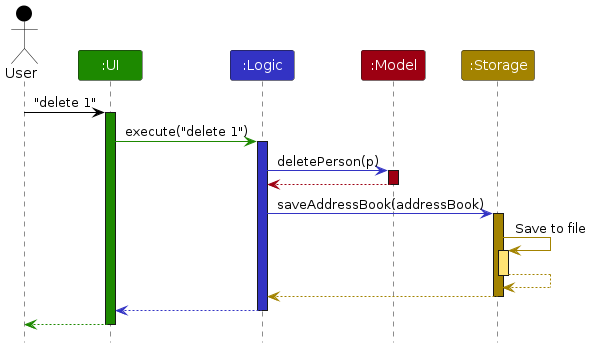
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
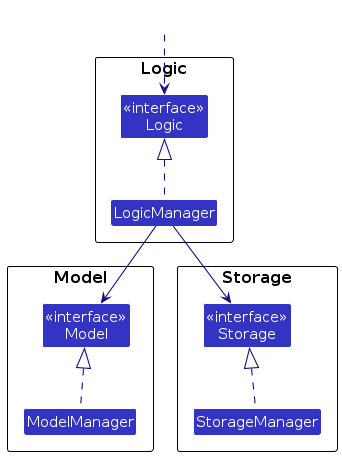
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
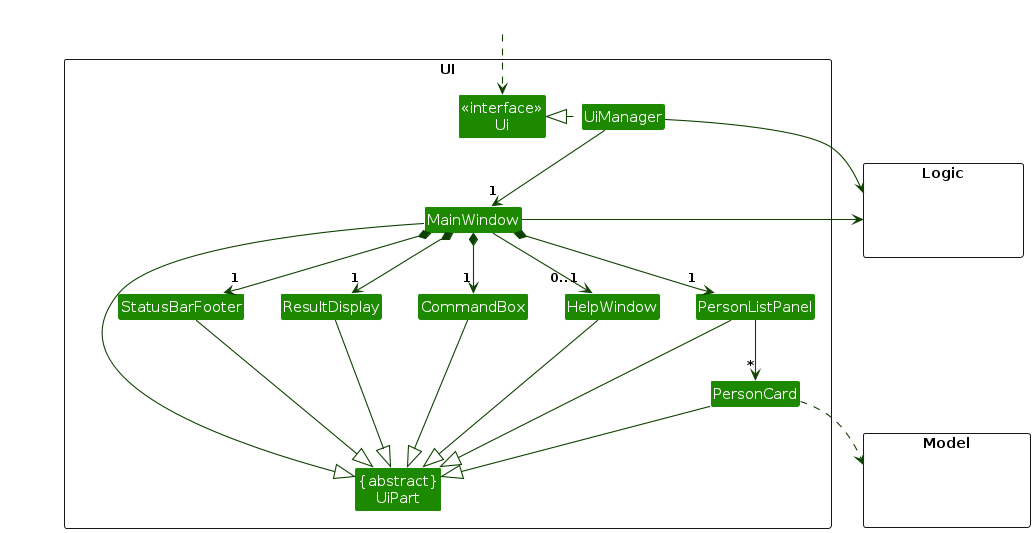
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
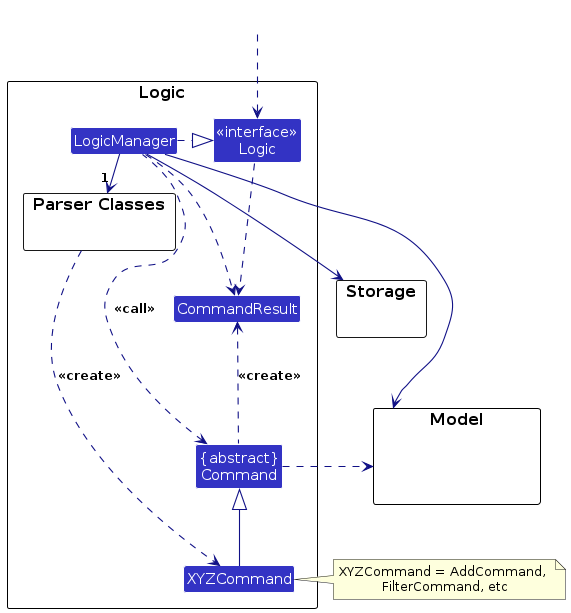
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
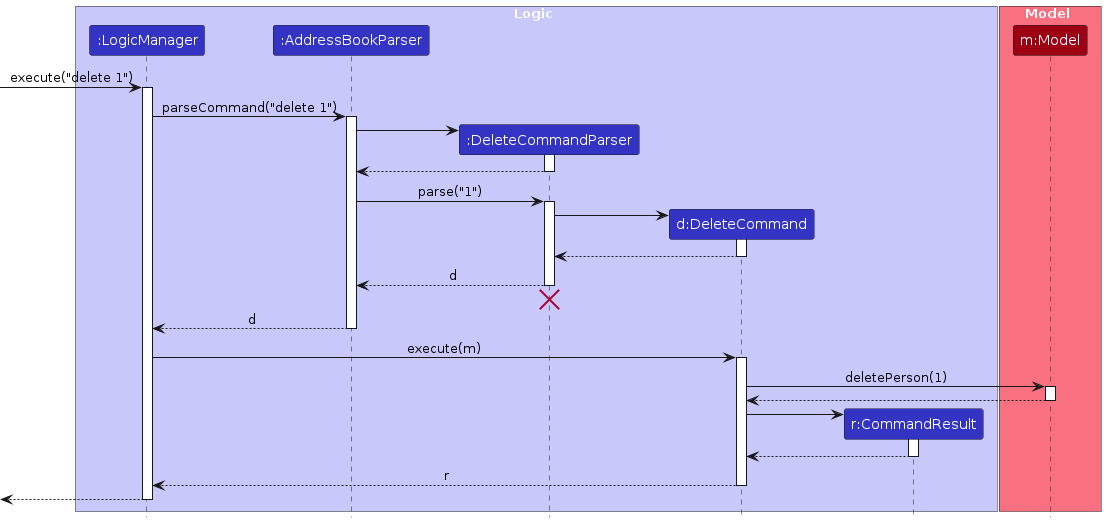
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
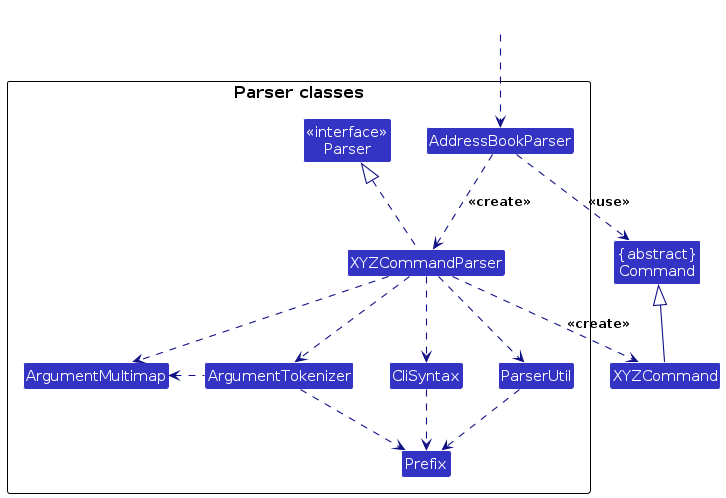
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
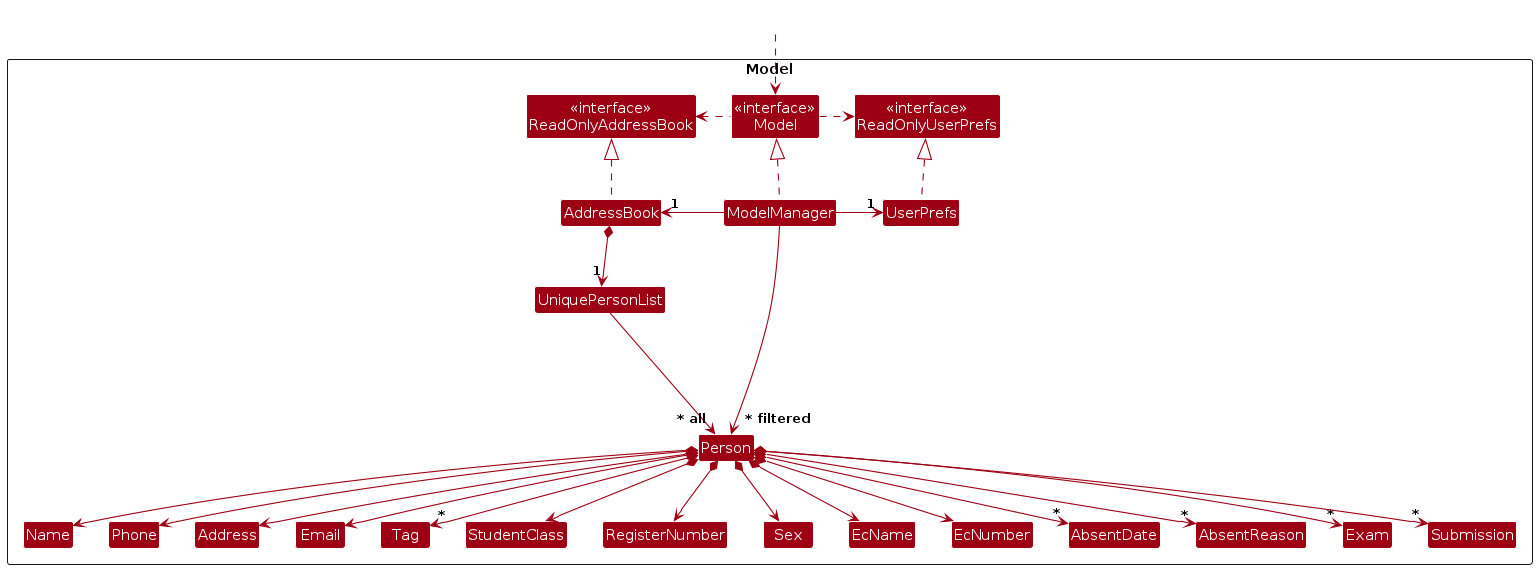
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.
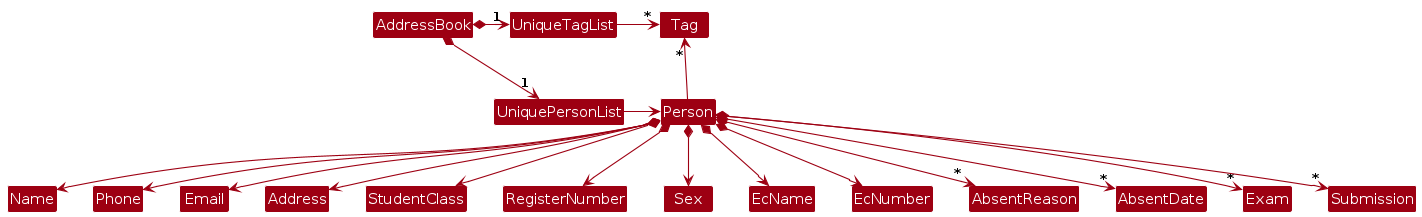
Storage component
API : Storage.java
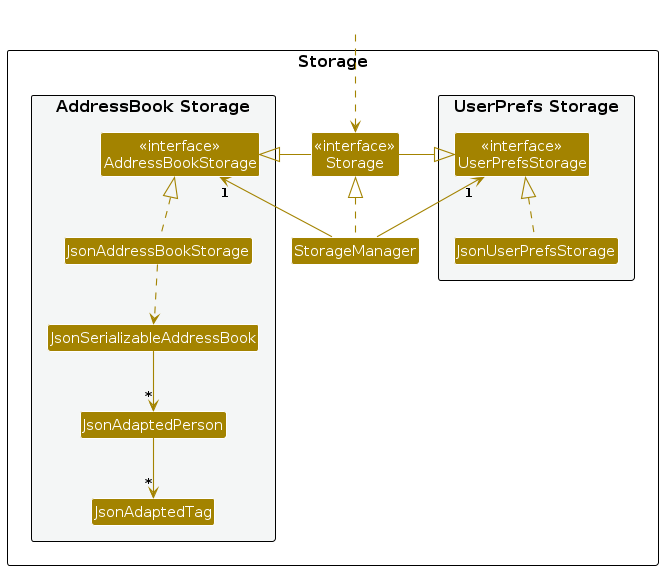
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
Proposed Implementation
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedAddressBook. It extends AddressBook with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an addressBookStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
VersionedAddressBook#commit()— Saves the current address book state in its history.VersionedAddressBook#undo()— Restores the previous address book state from its history.VersionedAddressBook#redo()— Restores a previously undone address book state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() and Model#redoAddressBook() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedAddressBook will be initialized with the initial address book state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single address book state.

Step 2. The user executes delete 5 command to delete the 5th person in the address book. The delete command calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing the modified state of the address book after the delete 5 command executes to be saved in the addressBookStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted address book state.
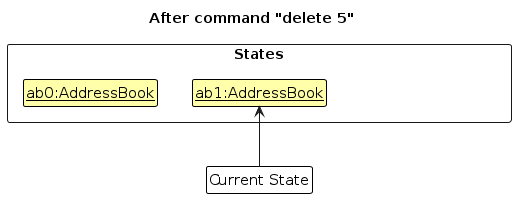
Step 3. The user executes add n/David … to add a new person. The add command also calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing another modified address book state to be saved into the addressBookStateList.
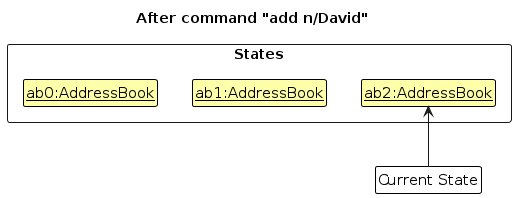
Note: If a command fails its execution, it will not call Model#commitAddressBook(), so the address book state will not be saved into the addressBookStateList.
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the person was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoAddressBook(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous address book state, and restores the address book to that state.
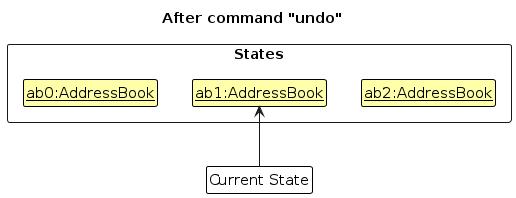
Note: If the currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial AddressBook state, then there are no previous AddressBook states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather
than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how an undo operation goes through the Logic component:
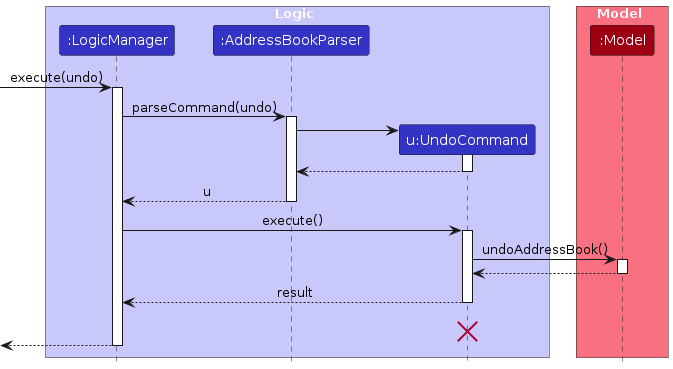
Note: The lifeline for UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
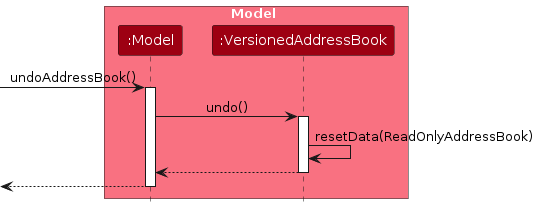
Similarly, how an undo operation goes through the Model component is shown below:
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoAddressBook(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the address book to that state.
Note: If the currentStatePointer is at index addressBookStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest address book state, then there are no undone AddressBook states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the address book, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() or Model#redoAddressBook(). Thus, the addressBookStateList remains unchanged.
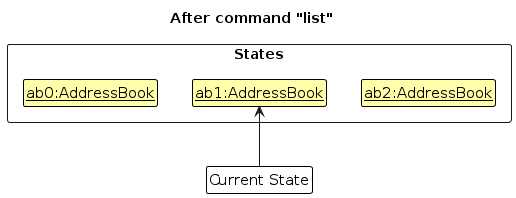
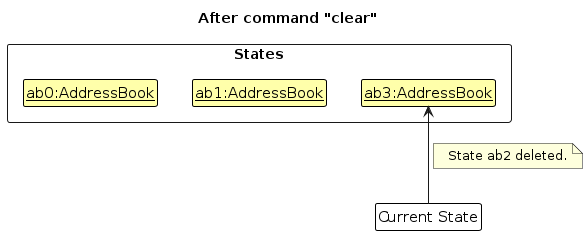
Step 6. The user executes clear, which calls Model#commitAddressBook(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the addressBookStateList, all address book states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add n/David … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
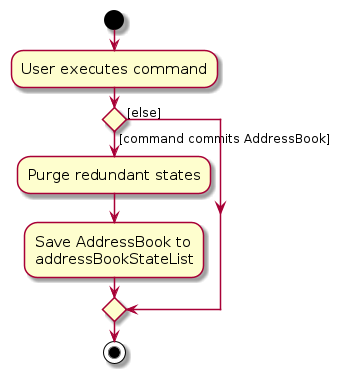
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
Design considerations:
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire address book.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the person being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- secondary school teacher
- many students to track
- many tests and submissions to track
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: track students’ test scores, submissions, progress and also, access their particulars with ease, all in one place!
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | prepared teacher | add student's email | email the student when I need to |
* * * | caring teacher | add student's name | call a student by his/her name |
* * * | efficient teacher | add student's register number | identify a student more quickly |
* * * | teacher wanting to split students for group project | add student's sex | see how many students of each gender I have |
* * * | caring teacher | add student's address | visit a student who may be sick at home |
* * * | prepared teacher | add student's contact number | call up the student when I need to contact him/her |
* * * | prepared teacher | add student's emergency contact name | identify the person I am calling if there are emergencies |
* * * | prepared teacher | add student's emergency contact number | notify the person in case of emergencies |
* * * | prepared teacher | add student's class | identify which student is in which class |
* * * | diligent teacher | remove a student from the app | ensure my records are accurate when they are no longer in the class |
* * | caring teacher | add student's photo | know what my students look like |
* * | lazy teacher | mass add student information | save the trouble of adding them one by one |
* * | lazy teacher | mass delete all dummy data | save the trouble of removing them one by one |
* * | diligent teacher | assign roles to students | manage students with the specific roles |
* * | neat teacher | group students by their class | manage and access information by class |
* * | teacher wanting to split students for group project | separate students into project groups | manage their project work within the app |
* * | prepared teacher | update a student's information | have the most current details when there is a change |
* * | diligent teacher | assign progress tags to individual students | categorise their performance in class |
* * | efficient teacher | sort the students by name | arrange the students lexicographically for exam conditions |
* * | caring teacher | add a comment for a student | take note of that student's particular trait |
* * | strict teacher | track a student's submissions | see which students did not submit tasks on time |
* * | strict teacher | track student attendance | address absenteeism and its impact on student performance |
* * | diligent teacher | add a new test for all my students | keep track of all the students' results |
* * | diligent teacher | add the scores of the students | have an overview of everyone's results |
* | picky teacher | customize the app settings | align the configuration with my preferences |
* | teacher who likes to have everything in one app | create a seating arrangement for the class | edit the seating arrangement any time |
* | diligent teacher | export information of all my graduated students | store them into the school database |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the StudentManagerPro and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC01 Add Student's Name
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's name is added to the system and can be used to track their academic progress.
- If an invalid name is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's name to the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the student to the system.
- System adds the student name to the student profile.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid name command format, with no special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid name command format, with no special characters.
3a. User leaves the name field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid name.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid name.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC02 Add Student's Email
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's email is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid email is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's email to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the email to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid email command format, with no special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid email command format, with no special characters.
3a. User leaves the email field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid email.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid email.
3b. User enters a duplicate email.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the email already exists in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the email already exists in the system.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC03 Add Student's Register Number
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's register number is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid register number is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's register number to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the register number to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid register number command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid register number command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the register number field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid register number.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid register number.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC04 Add Student's Sex
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's sex is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid sex is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's sex to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the sex to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid sex command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid sex command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the sex field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid sex.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid sex.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC05 Add Student's Address
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's address is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid address is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's address to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the address to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid address command format, with only acceptable
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid address command format, with only acceptable
special characters.
3a. User leaves the address field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid address.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid address.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC06 Add Student's Contact Number
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's contact number is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid contact number is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's contact number to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the contact number to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid contact number command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid contact number command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the contact number field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid contact number.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid contact number.
3b. User enters a duplicate contact number.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the contact number already exists in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the contact number already exists in the system.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC07 Add Student's Emergency Contact Name
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's emergency contact name is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid name is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's emergency contact name to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the emergency contact name to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact name command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact name command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the emergency contact name field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact name.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact name.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC08 Add Student's Emergency Contact Number
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's emergency contact number is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid contact number is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's emergency contact number to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the emergency contact number to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact number command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact number command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the emergency contact number field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact number.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid emergency contact number.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC09 Add Student's Class
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student profile has been created through the addition of the student name(UC01).
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's class is added to the student profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid class is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add a student's class to a student's profile in the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System adds the class to the student profile in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid class command format, with no
special characters.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid class command format, with no
special characters.
3a. User leaves the class field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid class.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid class.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC10 Remove Student from the System
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student to be removed exists in the system.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student will be removed from the system.
- If student does not exist or an invalid input is entered, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to remove a student from the StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the input.
- System removes the student from the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index command format.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index command format.
3a. User leaves the index field empty.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index.
3b. User enters an index that does not exist in the system.
- 3b1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index of a student in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message to ask for a valid index of a student in the system.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC11 Add Student's Attendance
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student is already added in the system.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the attendance record for the student is added to the system and can be used to track their attendance history.
- If invalid data or reason is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add attendance for a student in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input’s format.
- System validates the attendance data.
- System adds the attendance record to the student’s profile.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the attendance data.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid attendance format.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid attendance format.
3a. User leaves the absent reason blank (indicating deletion of attendance).
- 3a1. System deletes the attendance record for that entry, and displays a confirmation message.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System deletes the attendance record for that entry, and displays a confirmation message.
3b. User enters absent date in an invalid format.
- 3b1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent date format.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent date format.
3c. User enters a date that does not exist (e.g., 30-02-2024).
- 3c1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent date.
Use case ends
- 3c1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent date.
3d. User enters absent reason in an invalid format.
- 3d1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent reason format.
Use case ends.
- 3d1. System displays an error message asking for a valid absent reason format.
3e. User tries to add attendance for a student that does not exist.
- 3e1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3e1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
3f. User tries to add multiple attendances for a student at one go.
- 3f1. System displays an error message notifying that input with multiple attendances is not allowed.
Use case ends.
- 3f1. System displays an error message notifying that input with multiple attendances is not allowed.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC12 Add Exam
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Existing students in the system to add exams for.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the exam is added for all students currently in the system with a score of "NIL".
- If an invalid exam name is given as input, an error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add exam in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the exam data.
- System adds the exam to every student currently in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the exam name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
3a. User tries to add an exam that already exists in the system.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the exam already exists.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the exam already exists.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC13 Add Student's Exam Score
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student is already added in the system.
- Exam already added for student.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's exam score is added to the specified exam in the student's profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid exam name or exam score is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add the score for a particular exam for a student in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the exam data.
- System adds the exam score to the specified exam in the student's profile.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the exam name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
2b. User enters invalid characters in the exam score.
- 2b1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam score format, an integer between 0 and 100.
Use case ends.
- 2b1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam score format, an integer between 0 and 100.
3a. User tries to add a score to an exam that does not exist.
- 3a1. System displays an error message notifying that the exam does not exist in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message notifying that the exam does not exist in the system.
3b. User tries to add a score to an exam for a student that does not exist.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
3c. User tries to add a score to an exam for a student that is the same as is already recorded in the system for the same exam of the same student.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the exam score is not changed.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the exam score is not changed.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC14 Delete an Exam
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Exam exists in the system for students.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the exam is deleted from all students currently in the system.
- If an invalid exam name is given as input, an error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to delete exam in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the exam data.
- System deletes the exam from every student currently in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. User enters invalid characters in the exam name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid exam name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
- 3a. User tries to delete a exam that does not exist in the system.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the exam does not exist.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the exam does not exist.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC15 Add a Submission
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Existing students in the system to add exams for.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the submission is added for all students currently in the system with a status of "NIL".
- If an invalid submission name is given as input, an error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add submission in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the submission data.
- System adds the submission to every student currently in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the submission name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
3a. User tries to add a submission that already exists in the system.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the submission already exists.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the submission already exists.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC16 Add a Student's Submission Status
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Student is already added in the system.
- Submission already added for student.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the student's submission status is added to the specified submission in the student's profile and saved in the system.
- If an invalid submission name or submission status is given as input, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to add the status for a particular submission for a student in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the submission data.
- System adds the submission status to the specified submission in the student's profile.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the submission name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
2b. User enters invalid characters in the submission status.
- 2b1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission status format, "Y", "N" or "NIL".
Use case ends.
- 2b1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission status format, "Y", "N" or "NIL".
3a. User tries to add a status to a submission that does not exist.
- 3a1. System displays an error message notifying that the submission does not exist in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message notifying that the submission does not exist in the system.
3b. User tries to add a status to a submission for a student that does not exist.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the student does not exist in the system.
3c. User tries to add a status to a submission for a student that is the same as is already recorded in the system for the same submission of the same student.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the submission status is not changed.
Use case ends.
- 3b1. System displays an error message notifying that the submission status is not changed.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC17 Delete a Submission
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
- Submission exists in the system for students.
Guarantees:
- If successful, the submission is deleted from all students currently in the system.
- If an invalid submission name is given as input, an error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to delete submission in StudentManagerPro.
- System validates the input's format.
- System validates the submission data.
- System deletes the submission from every student currently in the system.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. User enters invalid characters in the submission name.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid submission name format, with only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
3a. User tries to delete a submission that does not exist in the system.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the submission does not exist.
Use case ends.
- 3a1. System displays an error message telling the user that the submission does not exist.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC18 Sort Students
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
Guarantees:
- If successful, student list displayed will be sorted.
- If an invalid attribute is given, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to sort students based on a particular attribute.
- System validates the input attribute.
- System sorts the displayed list based on the attribute.
- System displays the sorted list.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. System detects an invalid attribute.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid input.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message asking for valid input.
System: StudentManagerPro
Use case: UC19 Filter Students
Actor: User
Preconditions:
- StudentManagerPro is open.
Guarantees:
- If successful, student list displayed will be filtered according to the predicate provided.
- If an invalid predicate or format is given, a corresponding error message is displayed.
MSS
- User gives the command to filter students with specific predicates by one or multiple attributes.
- System validates the input predicates.
- System filters the student list based on the provided predicates.
- System displays the filtered list.
- System confirms the success by displaying a success message stating the number of filtered students.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. User inputs a filter command that is incomplete with no prefixes mentioned.
- 1a1. System displays an error message showing the correct format of the filter command.
Use case ends.
- 1a1. System displays an error message showing the correct format of the filter command.
1b. User tries to filter by a predicate that is not supported by the filter functionality.
- 1b1. System displays an error message that shows the attributes supported by the filter command and corresponding prefixes.
Use case ends.
- 1b1. System displays an error message that shows the attributes supported by the filter command and corresponding prefixes.
2a. System detects an empty predicate value after the attribute prefix.
- 2a1. System displays an error message stating that predicates cannot be empty.
Use case ends.
- 2a1. System displays an error message stating that predicates cannot be empty.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
17or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 persons without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should be for a single user (i.e. not a multi-user product).
- Data should be stored locally and should be in a human editable text file.
- Should not use DBMS to store data.
- Should follow the Object-oriented paradigm primarily.
- Should work without requiring an installer.
- Should not depend on any remote server.
- Use of third-party frameworks/libraries/services is subject to approval by the teaching team.
- GUI should work well (i.e., should not cause any resolution-related inconveniences to the user) for standard screen resolutions 1920x1080 and higher and for screen scales 100% and 125%. In addition, the GUI should be usable (i.e., all functions can be used even if the user experience is not optimal) for resolutions 1280x720 and higher and for screen scales 150%.
- Should be packaged into a single JAR file not exceeding 100MB.
- Documents should not exceed 15MB/file.
- DG and UG should be PDF-friendly (no expandable panels, embedded videos, animated GIFs etc.).
- Should primarily take in command line interface (CLI) inputs (i.e. input should primarily be text commands with minimal non-CLI inputs such as clicking).
- All user operations should complete within 100 ms.
- Product should be developed in a breadth-first incremental manner over the project duration.
- Final product should be a result of evolving/enhancing/morphing the given codebase.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- DBMS (Database Management System): Software for storing, retrieving, and managing data
- Developer Guide (DG): A document that provides technical details about the product's design and implementation
- User Guide (UG): A document that provides instructions for users on how to use the product's features
- CLI (Command Line Interface): An interface where the user types commands to interact with the software
- Class Grouping: The division of students into their respective classes, which can be managed and organized in the app for easy access
- Project Grouping: The arrangement of students into smaller groups for project purposes
- Tags: Labels assigned to students to indicate specific roles or characteristics
- Student Profile: A record within the system that contains information about a specific student
- EcName: Emergency contact name of a student
- EcNumber: Emergency contact number of a student
- SortAttribute: Particular attribute of a student that can be compared for sorting purposes
- Predicate: A condition that evaluates to true or false, used to filter or match specific items
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
Saving window preferences
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Adding a student
Adding a student into the list
Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/1 s/M c/2A
Expected: Student is added to the list. Details of the new contact shown in the status message.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/1 s/L c/2A
Expected: No student is added. Error detail regarding sex is shown in the status message.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/41 s/M c/2A
Expected: No student is added. Error detail regarding register number is shown in the status message.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/1 s/M c/A
Expected: No student is added. Error detail regarding class is shown in the status message.Other incorrect add commands to try:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/1 s/ c/2A
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/ s/M c/2A
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 r/1 s/M c/
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting a student
Deleting a student while all students are being shown
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list.Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message.Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No student is deleted. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete
delete x
...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Editing a student
Editing a student while all students are being shown
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list.Test case:
edit 1 c/1A
Expected: First student's class is changed. Details of the edited student shown in the status message.Test case:
edit 1 c/A1
Expected: No student's detailed are changed. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect edit commands to try:
edit
edit 0
edit c/1A c/2A
edit x c/1A(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding EcName for a student
Adding EcName for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List must not be empty, student for which EcName is added should already be in the list.
Test case:
addEcName 1 en/Sally Ho
Expected: First student will have his emergency contact name added. Name and emergency contact name will be shown in the status message.Test case:
addEcName 1 en/
Expected: First student will have his emergency contact name deleted. Name of student with the emergency contact name deleted will be shown in the status message.Test case:
addEcName 1 en/John Doe
Expected: First student's emergency contact name will be updated to "John Doe". Name and emergency contact name will be shown in the status message.Other incorrect addEcName commands to try:
addEcName
addEcName hhhh en/Jack
Expected: An error message is shown which includes the correct format of the addEcName command to follow.
Adding EcNumber for a student
Adding EcNumber for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List must not be empty, student for which EcNumber is added should already be in the list.
Test case:
addEcNumber 1 ep/91234567
Expected: First student will have his emergency contact number added. Name and emergency contact number will be shown in the status message.Test case:
addEcNumber 1 ep/
Expected: First student will have his emergency contact number deleted. Name of student with the emergency contact number deleted will be shown in the status message.Test case:
addEcNumber 1 ep/123 456
Expected: No emergency contact number is changed. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addEcNumber commands to try:
addEcNumber
addEcNumber abc ep/91234567
addEcNumber x ep/91234567(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding attendance for a student
Adding attendance for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list.Test case:
addAttendance 1 ad/24-09-2024 ar/MC
Expected: Attendance record with date 24-09-2024 and reason MC is added to the first student. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addAttendance 0 ad/24-09-2024 ar/MC
Expected: No attendance is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addAttendance commands to try:
addAttendance
addAttendance 1 ad/24-09-24 ar/MC
addAttendance 1 ad/24-09-2024 ar/!@#
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting attendance for a student
Deleting attendance for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list. The test for adding attendance should be done first as the student must have an existing attendance to be deleted.Test case:
addAttendance 1 ad/24-09-2024 ar/
Expected: Attendance record with date 24-09-2024 is deleted from the first student. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addAttendance 0 ad/24-09-2024 ar/
Expected: No attendance is deleted. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addAttendance commands to try:
addAttendance 1 ad/24-09-2024
addAttendance 1 ad/2024-12-12 ar/
addAttendance x ad/24-09-2024 ar/(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding exam for students
Adding exam for all students currently in the list
Test case:
addExam ex/Midterm
Expected: Exam with exam name Midterm is added to all students in the student list. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addExam ex/Midterm#
Expected: No exam is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addExam commands to try:
addExam
addExam ex/
addExam ex/#@*
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding exam score for a student
Adding exam score for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list. The test for adding exam should be done first as the student must have an existing exam to add an exam score to.Test case:
addExamScore 1 ex/Midterm sc/70.0
Expected: Exam with exam name Midterm is updated with a exam score of 70.0 for the first student. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addExamScore 1 ex/Midterm sc/101.0
Expected: No exam score is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addExamScore commands to try:
addExamScore 1 ex/Midterm
addExamScore 1 ex/Midterm sc/
addExamScore x ex/Midterm sc/70.0(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting exam for students
Deleting exam for all students currently in the list
Prerequisites: The test for adding exam should be done first as the students must have an existing exam to be deleted.
Test case:
deleteExam ex/Midterm
Expected: Exam with exam name Midterm is deleted from all students in the student list. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
deleteExam ex/Midterm#
Expected: No exam is deleted. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect deleteExam commands to try:
deleteExam
deleteExam ex/
deleteExam ex/#@*
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding submission for students
Adding submission for all students currently in the list
Test case:
addSubmission sm/Assignment 1
Expected: Submission with submission name Assignment 1 is added to all students in the student list. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addSubmission sm/Assignment #1
Expected: No submission is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addSubmission commands to try:
addSubmission
addSubmission sm/
addSubmission sm/#@*
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding submission status for a student
Adding submission status for a student in the list
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list. The test for adding submission should be done first as the student must have an existing submission to add a submission status to.Test case:
addSubmissionStatus 1 sm/Assignment 1 ss/Y
Expected: Submission with submission name Assignment 1 is updated with a submission status of Y for the first student. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
addSubmissionStatus 1 sm/Assignment 1 ss/A
Expected: No submission status is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect addSubmissionStatus commands to try:
addSubmissionStatus 1 sm/Assignment 1
addSubmissionStatus 1 sm/Assignment 1 ss/
addSubmissionStatus x sm/Assignment 1 ss/Y(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting submission for students
Deleting submission for all students currently in the list
Prerequisites: The test for adding submission should be done first as the students must have an existing submission to be deleted.
Test case:
deleteSubmission sm/Assignment 1
Expected: Submission with submission name Assignment 1 is deleted from all students currently in the list. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
deleteSubmission sm/Assignment #1
Expected: No submission is deleted. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect deleteSubmission commands to try:
deleteSubmission
deleteSubmission sm/
deleteSubmission sm/#@*
Expected: Similar to previous.
Filtering students
Filters all students currently in the list based on the specified attribute and predicate
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list.Test case:
filter n/John
Expected: Returns the students in the list who have John in their name. Confirmation message is shown in the status message, including the number of persons filtered.Test case:
filter n/John Park
Expected: Returns the students in the list who have John OR Park in their name. Confirmation message is shown in the status message, including the number of persons filtered.Test case:
filter n/John Park p/99999999 92929292
Expected: Returns the students in the list who match at least one name and one phone number. Confirmation message is shown in the status message, including the number of persons filtered.Test case:
filter hhh
Expected: Filtering does not occur and an error message is depicted to show the correct format of the filter command.Test case:
filter n/
Expected: Filtering does not occur and an error message is depicted to assert that the predicate values cannot be empty.Other incorrect sort commands to try:
filter n
filter n/ p/
Expected: Similar to previous
Sorting students
Sorts all students currently in the list based on the specified attribute
Prerequisites: List all students using the
listcommand. Multiple students in the list.Test case:
sort register number
Expected: List of students is sorted according to register number. Confirmation message shown in the status message.Test case:
sort abc
Expected: List is not sorted, Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect sort commands to try:
sort
sort 1
Expected: Similar to previous
Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Team size: 5
Ui
- Ui can be adjusted such that long names and phone numbers will not be truncated when added into StudentManagerPro.
Sex
- Sex attribute can be adjusted to be case insensitive in the future to make it more convenient for users.
Class
- Class attribute can be made more flexible by allowing different formats for identifying and distinguishing between classes.
EcName / EcNumber
- Combine
addEcNameandaddEcNumberinto one command.
Filter
- Allow filtering by phone numbers using predicates less than 3 digits long.
- Allow filtering for exact multi-word addresses. For example, using
filter a/Block 30 Geylangwill return only students with an address that exactly matchesBlock 30 Geylangrather than returning partial matches for individual words likeBlock,30, orGeylang
Sort
- Sort in descending order.
Exam / Submission
- Include the ability to assign specific exams and submissions to selected groups and not automatically to all students, allowing for customized tests and assignments for different sets of students.
- Exams and Submissions can be automatically added for new students being added to the list, instead of having the user add them manually.
Attendance
- As only dates in the current year are allowed when adding attendance, the command can be adjusted such that it only requires users to enter the date in the form of DD-MM.
Appendix: Effort
- The project required a significant amount of effort and focus to implement the new features.
- There were some challenges along the way when we did not know how to implement specific features such as filter and sort.
- It was also quite challenging to add new attributes and represent them as tables in the GUI, such as exams, submissions, and attendance.
- While AB3 deals with simple attributes of a person, we had to include attributes that were more complex and tailored for our application use and needs, thus requiring us to store more non-trivial data for every student.
- Some achievements of the project include learning the workflows of having multiple developers work on the same product and managing each other's changes.